GLP-1s and the Weight Regain Dilemma: What Happens Post-Treatment?
January 18, 2024
 1249
1249 
In the ever-evolving battle against obesity, GLP-1 treatments have emerged as a beacon of hope for those seeking weight loss solutions.
These treatments, renowned for their effectiveness in reducing body weight, have gained popularity rapidly.
However, beneath the surface of their apparent success lies a less discussed reality.
This blog aims to shed light on the negative aspects of GLP-1 treatments, delving into the significant side effects they entail and the common issue of weight regain after the treatment is discontinued.
We’ll explore why this seemingly promising solution may not be as ideal as it appears, particularly in the long term.

While GLP-1 treatments have been celebrated for their ability to aid in weight loss, they come with a range of side effects that can significantly impact the users’ quality of life.
Common Adverse Effects
Users of GLP-1 treatments often report various gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation, which can be distressing and debilitating.
These side effects are not only uncomfortable but can also lead to decreased appetite and altered eating patterns, sometimes contributing to the initial weight loss observed.
Serious Health Risks
Beyond these discomforts, there are more serious health risks associated with GLP-1 treatments.
One such concern is the potential risk of pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas that can be severe and life-threatening.
Other reported adverse effects include gallbladder issues, kidney problems, and even potential links to thyroid cancer, though research in these areas is ongoing.
Impact on Overall Health and Well-being
The burden of these side effects can be substantial, affecting not just physical health but also the mental and emotional well-being of individuals undergoing treatment.
For some, the severity of these side effects leads to discontinuation of the treatment, while for others, it results in a constant struggle to balance the benefits of weight loss against the drawbacks of the treatment’s adverse effects.

The journey of weight loss via GLP-1 treatments often starts with promise and optimism.
However, the reality of this weight loss path is more complex and less permanent than it initially appears.
Temporary Nature of Weight Loss
Individuals on GLP-1 therapy typically experience significant weight loss, particularly in the initial stages of the treatment.
This early success can be attributed to the drug’s ability to suppress appetite and, consequently, reduce caloric intake.
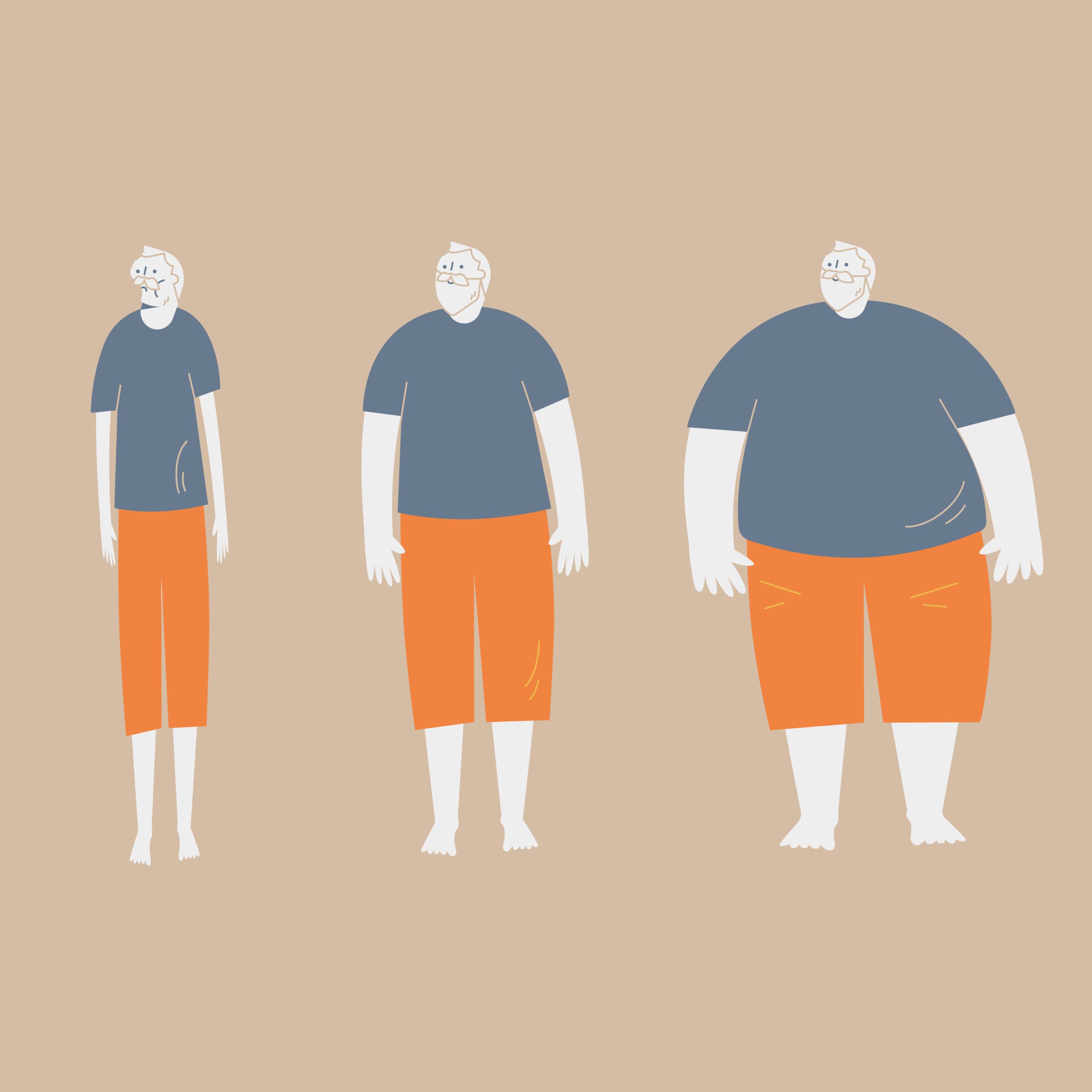
Despite these initial results, the weight loss achieved with GLP-1s is often not sustainable in the long term.
Once the treatment is discontinued, the weight tends to return, sometimes even surpassing the original baseline weight.
Addressing Symptoms, Not Causes
A critical aspect of GLP-1 treatments is that they primarily manage the symptoms of obesity – such as excessive appetite – rather than addressing the root causes.
Factors like eating habits, lifestyle choices, and genetic predispositions that contribute to obesity are not directly targeted by these treatments.
Therefore, without a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, the effectiveness of GLP-1s in long-term weight management is limited.
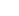
One of the most disheartening aspects of GLP-1 treatments is the common occurrence of weight regain after the cessation of therapy, a phenomenon backed by both physiological evidence and clinical studies.
Physiological Factors Leading to Weight Regain
The body responds to weight loss achieved through GLP-1 treatments by adjusting its metabolic rate and appetite regulation mechanisms.
Once the treatment stops, these adjustments can lead to an increased appetite and a slower metabolism, making weight maintenance challenging.
The cessation of GLP-1 therapy often results in the return of hunger levels to pre-treatment states or even higher, driving increased food intake and subsequent weight gain.
Prevalence of Weight Regain
Studies and clinical observations have consistently shown a high rate of weight regain among individuals post-GLP-1 treatment cessation.
This pattern is not only prevalent but also a significant concern for healthcare providers and patients, as the regained weight can sometimes exceed the initial weight loss, leading to a worse metabolic state than before the treatment.

The aftermath of discontinuing GLP-1 treatments often leads to more than just the physical aspect of weight regain; it can plunge individuals into a state that is arguably worse than their starting point.
Physical and Psychological Impacts of Rebound Weight Gain
Physically, the rebound weight gain can be rapid and demoralizing, often leading to higher body weight than before the treatment.
This can exacerbate obesity-related health issues like hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular risks.
Psychologically, this weight regain can be devastating.
Many individuals experience feelings of failure and frustration, having initially seen significant weight loss success.
The cycle of losing and regaining weight can also lead to a sense of hopelessness and helplessness, impacting mental health and self-esteem.
It can undermine the motivation to pursue further weight management efforts, trapping individuals in a detrimental cycle.
Dealing with Recurring Health Issues
The recurrence of obesity-related health issues, intensified by the additional weight gain, poses further challenges.
It can lead to a sense of despair and resignation, particularly for those who viewed GLP-1 treatments as their last resort for weight management.
As we conclude this exploration of GLP-1 weight loss treatments, it’s clear that while they offer a temporary solution, the long-term consequences are far from ideal.
The Negative Cycle of Side Effects and Weight Regain
GLP-1 treatments, despite their initial effectiveness, often lead to a negative cycle of significant side effects and subsequent weight regain after the cessation of treatment.
This cycle not only affects physical health but also has profound psychological implications, impacting the overall well-being of individuals.
The Importance of a Comprehensive Approach
Understanding the full scope of outcomes associated with GLP-1 treatments is crucial for anyone considering this path for weight loss.
It underscores the need for sustainable weight management approaches that go beyond temporary solutions and address the underlying causes and lifestyle factors contributing to obesity.
A holistic approach, incorporating lifestyle changes, behavioral modifications, and possibly alternative medical treatments, is essential for long-term success in weight management.
In summary, GLP-1 treatments should be approached with caution and awareness of their limitations.
Sustainable weight loss requires a comprehensive, multifaceted approach that considers both physical health and psychological well-being.

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]