Consumers of GLP-1 Drugs and Ozempic Report Suicidal and Self-Harm Thoughts
July 31, 2023
 1010
1010 
In the realm of modern medicine, the battle against Type 2 diabetes and obesity continues to be one of the most prominent challenges.
With millions suffering globally, the need for effective treatments is paramount.
Among the innovative solutions in recent years are GLP-1 (Glucagon-like Peptide-1) drugs, which have emerged as a significant player in this field.
However, like with many medications, unexpected concerns can surface.
Recent reports have raised questions regarding a potential connection between GLP-1 drugs and suicidal or self-harm thoughts.
While alarming, it’s essential to recognize that these concerns are in the early stages of investigation and should be treated with careful consideration.
In light of these concerns, both the UK’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have launched investigations.
These bodies are diligently working to ascertain whether these reports are indicative of a broader pattern, requiring possible regulatory action.
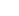
GLP-1 drugs, or Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists, play a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels.
They work by mimicking the action of the natural hormone GLP-1, which stimulates the release of insulin, inhibits the release of glucagon, and slows down digestion.
The combined effect helps manage glucose levels in people with Type 2 diabetes.
Among the various GLP-1 drugs on the market, Ozempic has become particularly well-known.
With proven efficacy in controlling blood sugar levels, it’s a widely prescribed option for those dealing with Type 2 diabetes.
GLP-1 drugs have become an essential part of the therapeutic landscape for Type 2 diabetes.
Not only do they help in managing blood sugar levels, but some, including Ozempic, have also demonstrated benefits in weight loss.
This dual action has made them a preferred choice for many healthcare providers, solidifying their position as a valuable treatment option.
In conclusion, the world of GLP-1 drugs represents a crucial advancement in the management of Type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Yet, as with any medical innovation, it also comes with questions and concerns.
The ongoing investigations into the potential connection with suicidal or self-harm thoughts emphasize the complexity of medical science and the importance of continued scrutiny and vigilance.

Recent headlines have been occupied with a perplexing concern related to GLP-1 drugs, particularly Ozempic.
Some reports have emerged, hinting at a possible connection between these drugs and thoughts of suicide or self-harm.
While the evidence is preliminary, the situation demands careful attention and scrutiny.
Although detailed information may still be under investigation, some individual cases have come to light.
These anecdotes, while not conclusive, have raised valid questions that merit exploration.
They serve as a reminder that even the most trusted treatments can present unforeseen challenges, and continual monitoring is essential.
Understandably, these reports have elicited mixed reactions from both healthcare providers and patients.
While some medical professionals express caution and call for a comprehensive examination, others advocate for maintaining perspective and not jumping to conclusions.
Patients, on the other hand, are faced with a challenging balance between following prescribed treatments and considering potential risks, all under the guidance of their healthcare providers.

The UK’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has acted promptly in light of the emerging concerns.
A focused review is underway regarding Ozempic and its potential link to suicide and self-harm risks.
This process involves rigorous analysis of existing data, clinical studies, and patient feedback to determine if regulatory action is warranted.
Similarly, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has commenced an investigation into GLP-1 drugs’ potential to induce suicidal thoughts, particularly in the context of weight loss.
Recognizing the gravity of the situation, the EMA is collaborating with various stakeholders to ensure a thorough and unbiased evaluation of the facts.
Though responses from drug manufacturers may vary, it is expected that they will cooperate fully with regulatory bodies.
They likely recognize the critical importance of patient safety and are committed to supporting transparent investigations.
Their participation, including sharing necessary data and insights, is vital in arriving at a clear understanding of the situation.
In summary, the concerns regarding GLP-1 drugs and their potential link to suicidal or self-harm thoughts have set in motion a series of responses from various stakeholders.
While the situation is complex and evolving, it underscores the dynamic nature of medical science and the imperative for vigilance, transparency, and collaboration in ensuring patient well-being.
The connection between GLP-1 drugs and suicidal or self-harm thoughts is a novel concern, and as such, existing research on the topic might be limited.
However, it is vital to explore previous studies on similar subjects or closely related areas that may provide insights into the current situation.
This exploration could include examining the broader effects of diabetes medications on mental health.
Medical professionals from different specializations, including endocrinologists and mental health experts, have weighed in on the matter.
While endocrinologists may focus on the pharmacological aspects, mental health experts can provide insights into the psychological dimension.
The consensus is generally that more investigation is needed, and caution is advised in drawing conclusions without substantial evidence.
While the exact mechanism linking GLP-1 drugs to suicidal thoughts is yet to be established, some hypotheses might be explored.
These could include examining the impact of these drugs on neurotransmitter activity, hormonal balances, or even considering indirect effects such as those related to weight loss and self-image.
It is a complex issue that requires multidisciplinary research and understanding.

For patients currently taking GLP-1 drugs, the best course of action is to consult with healthcare providers for personalized advice.
The individualized assessment of risk and benefit is vital, and abrupt changes in medication without professional guidance should be avoided.
Open communication with healthcare providers will help ensure a safe and appropriate approach.
If the situation demands, consideration of alternative treatment options may be explored in consultation with healthcare providers.
This process should be approached with care, weighing the pros and cons of different therapies, and ensuring alignment with the overall treatment goals for Type 2 diabetes or obesity management.
In conclusion, the intersection of science and practical guidance paints a picture of cautious consideration and patient-centered care.
While the scientific community strives to unravel the complexities of this situation, patients and healthcare providers must navigate the path with empathy, information, and collaboration.
These unfolding events reaffirm the perpetual need for vigilance and adaptability in the ever-evolving landscape of medical science and healthcare.

GLP-1 drugs, particularly Ozempic, have become household names in the battle against Type 2 diabetes and obesity.
However, recent reports and subsequent investigations into potential connections with suicidal or self-harm thoughts have brought a new dimension of complexity to this medical field.
From the emerging concerns to the scientific perspectives and practical implications, this issue underscores the multifaceted nature of medical science.
It’s crucial to note that the investigations into this matter are ongoing.
Conclusive evidence is yet to be presented, and as such, drawing premature conclusions would be unwise.
The situation highlights the ever-present need for rigorous scientific research and the continuous reassessment of medical treatments in light of new information.
For readers who may be directly or indirectly affected by this issue, staying informed is key.
Regular consultation with healthcare professionals who are up-to-date with the latest developments ensures that treatment decisions are made with the best available information.
Open dialogue, collaboration, and personalized care should guide the way forward.
The unfolding story of GLP-1 drugs and the concerns regarding suicidal thoughts serves as a vivid reminder of the dynamic and complex nature of medical practice.
As we seek to enhance the quality of life through medical innovation, we must also remain vigilant, adaptive, and ever-curious.
The pursuit of knowledge and the commitment to patient well-being continue to guide us through uncharted territories, ever forward.

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]