The Comprehensive Guide to Cannabinoids and Their Unique Health Properties
December 11, 2023
 744
744 
Welcome to the fascinating world of cannabinoids, nature’s own chemical powerhouses found in the cannabis plant.
These remarkable compounds have captured the attention of scientists, medical professionals, and wellness enthusiasts alike.
But what exactly are cannabinoids?
In simple terms, they’re a group of compounds that interact with specific receptors in the human body, influencing everything from mood to pain perception.
In this journey, we’ll dive into the characteristics of the most well-known cannabinoids, unraveling their individual effects.
Whether you’re a curious newcomer or a seasoned cannabis connoisseur, this exploration will shed light on the diverse and often misunderstood world of these unique compounds.
So, let’s embark on this enlightening exploration together!
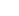
Description: Meet THC, the star of the cannabis world and undoubtedly the most famous cannabinoid.
It’s the primary psychoactive component in cannabis, responsible for the plant’s notorious reputation and its celebrated effects.
Effects: THC is a bit of a celebrity in the cannabinoid family, known for its ability to produce the euphoric “high” that many associate with cannabis use.
But there’s more to this compound than meets the eye.
It’s not just about the high; THC also boasts an array of potential therapeutic benefits.
It has been known to provide relief from chronic pain, a welcome effect for those suffering from various painful conditions.
For individuals battling a lack of appetite or dealing with nausea, especially in the context of chemotherapy, THC can be a game-changer, stimulating hunger and reducing nausea.
Its multifaceted nature makes THC not just a source of recreation, but also a potential ally in the world of medicinal cannabis.
Stay tuned as we delve into more cannabinoids, each with its own unique story and benefits!
Description: Step aside, THC, and make way for CBD, a cannabinoid that’s been making waves without the psychoactive splash.
Unlike its more famous cousin, CBD doesn’t induce a high, making it an appealing option for those seeking the benefits of cannabis without the altered state of mind.
Effects: CBD has emerged as a kind of a superhero in the wellness world, lauded for its potential to soothe the mind and body.
It’s like a Swiss Army knife in the world of cannabinoids, showing promise in a variety of areas.
Struggling with anxiety or feeling the weights of depression? CBD might offer some relief.
And it doesn’t stop there.
From chronic pain warriors to those battling inflammation, CBD steps in as a potential source of comfort and relief.
Its versatility and non-psychoactive nature have catapulted it to fame in the realm of health and wellness, making it a popular choice for a wide array of users.
Description: Now, let’s turn our attention to CBN, a milder member of the cannabinoid family.
Think of CBN as THC’s less intense sibling – it’s formed when THC ages and loses its punch.
It’s not the cannabinoid that grabs headlines, but it certainly has its charm.
Effects: CBN might not be the life of the party, but it’s the one you want to turn to when you need some rest.
Known for its sedative qualities, CBN is the unsung hero for those struggling to catch some Zs.
It’s like a gentle lullaby in cannabinoid form, potentially aiding in combatting sleep disorders and ensuring a good night’s rest.
While more research is needed to fully understand its effects, CBN is emerging as a potential go-to for a natural sleep aid, adding another dimension to the therapeutic uses of cannabis.
As we continue our journey through the world of cannabinoids, it’s clear that each compound has its unique role to play.
Stay with us as we uncover more about these fascinating substances!
Description: Meet CBG, often hailed as the “mother” of cannabinoids.
This is where it all begins – CBG is the chemical parent to THC and CBD, making it a cornerstone in the cannabinoid family.
Unlike its more famous offsprings, CBG is non-psychoactive, meaning it won’t get you high but will definitely pique your interest with its unique properties.
Effects: CBG might not be a household name yet, but it’s making strides in the scientific community.
Think of it as a potent little package with a punch of benefits.
It’s been eyed for its potential antibacterial properties – a warrior in the fight against germs.
But that’s not all; CBG also steps into the ring with inflammatory bowel disease, offering a glimmer of hope for those battling this chronic condition.
And for the grand finale, there’s growing interest in its neuroprotective properties, making it a potential player in brain health.
CBG may be the underdog of cannabinoids, but it’s definitely one to watch.
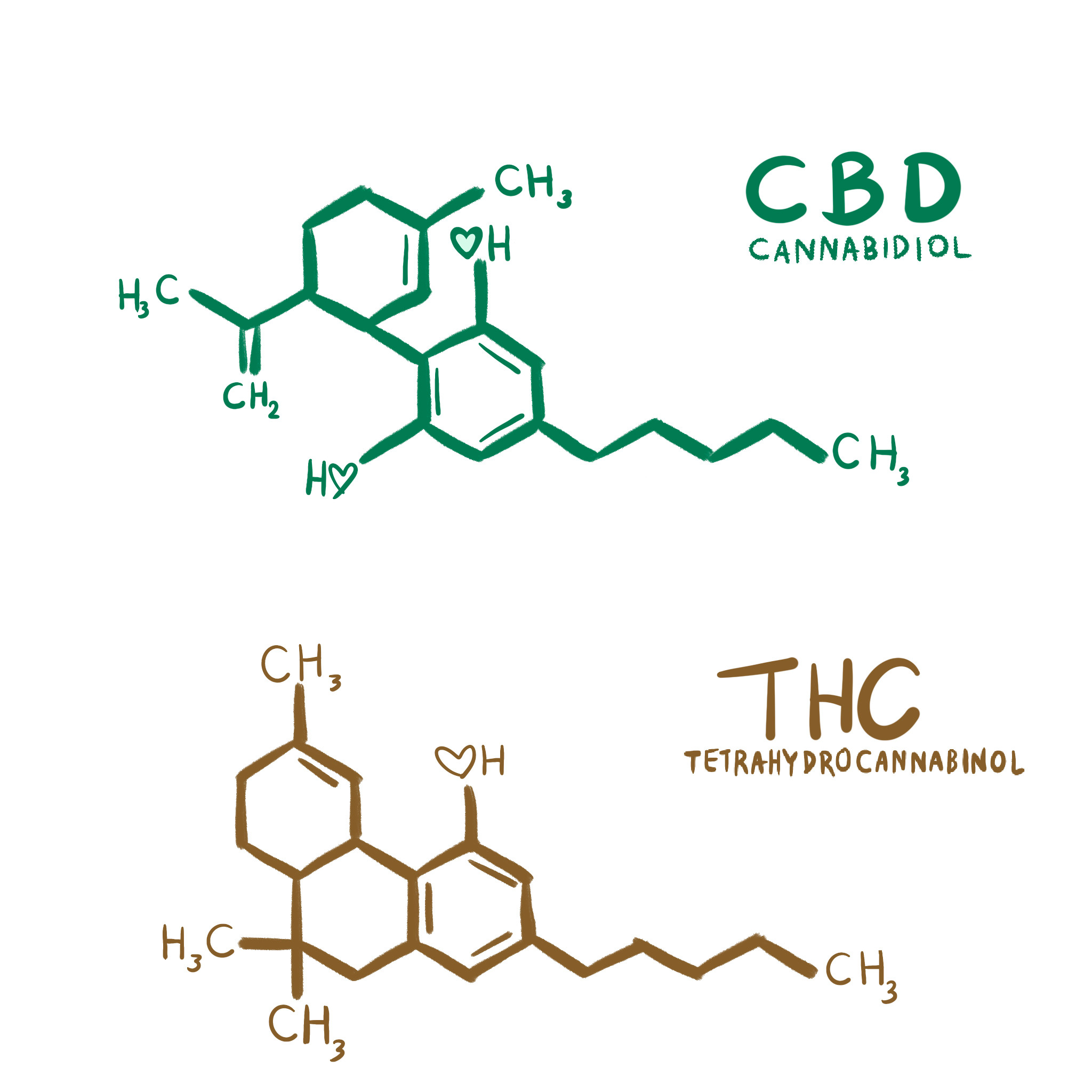
Description: Now, let’s talk about THCV, a compound similar to THC but with a twist.
It’s like THC’s cousin who attended a different college – related, yet distinctly unique.
THCV shares some of THC’s psychoactive properties, but it’s not just a simple copycat.
Effects: If THC is known for stimulating appetite (hello, munchies!), THCV is its opposite – a potential appetite suppressant.
This makes it an intriguing subject for weight management research.
But wait, there’s more: THCV also shows promise in regulating blood sugar levels, making it a compound of interest in the study of diabetes.
It’s like the cannabinoid that’s breaking the mold, offering a different set of benefits that challenge our understanding of cannabis and its effects.
As we continue to explore the diverse and complex world of cannabinoids, it becomes evident that each compound has a unique story and potential.
The variety and depth of effects these cannabinoids offer are not just intriguing but also a testament to the complexity of the cannabis plant and its interaction with our bodies.
Stay tuned for more enlightening insights into the world of cannabinoids!
Description: Let’s shine a light on CBC, a lesser-known yet fascinating member of the cannabinoid family.
Unlike the star-studded THC, CBC flies under the radar, but don’t let its low profile fool you.
This non-psychoactive compound might not induce a high, but it certainly has high potential in the world of wellness.
Effects: CBC emerges as a quiet contender in the realm of pain relief and anti-inflammatory action.
Imagine a gentle yet powerful force working behind the scenes to soothe aches and reduce swelling.
It’s like having a discreet but effective ally in your corner, fighting inflammation and discomfort without the psychoactive effects.
While it may not have the fame of its counterparts, CBC’s potential in contributing to pain management and reducing inflammation marks it as a cannabinoid worth knowing about.
Description: Now, let’s introduce CBDV, a compound that shares a close resemblance to CBD but with its own unique twist.
CBDV is like a specialized version of CBD, with a particular focus on neurological health.
This makes it a rising star in the cannabinoid constellation, especially for those interested in brain health and neurological function.
Effects: The real excitement around CBDV lies in its potential role in neurological disorders.
Current research is buzzing with the possibility of CBDV being a game-changer in treating epilepsy.
Imagine a natural compound offering a new ray of hope for those affected by seizures and other neurological conditions.
CBDV’s promise in this area is not just encouraging; it’s a beacon of potential in the ongoing exploration of cannabinoids and their therapeutic applications.
Its study is a testament to the evolving understanding of how these compounds can impact our health in profound and specific ways.
As we delve deeper into the cannabinoid spectrum, the sheer diversity and potential of these compounds continue to amaze.
Each one, from THC to its raw form THCA, or CBD to CBDA, presents a unique facet of the cannabis plant’s incredible capabilities.
Stay with us as we explore further, uncovering the myriad ways these compounds can impact health and wellness.
Description: When you think of THC, you might imagine its psychoactive effects, but there’s more to the story with its precursor, THCA.
In its raw form, found in the fresh cannabis plant, THCA is non-psychoactive, offering a different side to the THC narrative.
It’s like meeting the milder, gentler version of a well-known personality.
Effects: THCA steps into the spotlight with its anti-inflammatory prowess, offering a natural way to combat inflammation without the high.
But that’s not all – it also plays a role as a potential neuroprotective agent, which could be a significant discovery in the world of brain health.
And for those battling nausea, THCA might just be a new friend, offering relief without the psychoactive effects of its famous counterpart.
It’s fascinating to see how the transformation from THCA to THC not only changes its psychoactive status but also shifts its potential health benefits.
Description: Now let’s turn to CBDA, the precursor to the much-lauded CBD.
Present in the raw cannabis plant, CBDA is like the first draft of a masterpiece – it’s the initial form before it becomes the CBD we commonly talk about.
While it might not get as much attention as CBD, CBDA is an intriguing compound in its own right.
Effects: CBDA has begun to emerge from the shadows of CBD, showing potential in areas like nausea relief and anxiety reduction.
Imagine a natural aid for those moments of unease or for those who face the discomfort of nausea.
CBDA could potentially be that gentle yet effective solution.
As research continues, the promise of CBDA in these areas highlights the ever-evolving understanding and appreciation of the diverse applications of cannabinoids.
As we delve deeper into the cannabinoid spectrum, the sheer diversity and potential of these compounds continue to amaze.
Each one, from THC to its raw form THCA, or CBD to CBDA, presents a unique facet of the cannabis plant’s incredible capabilities.
Stay with us as we explore further, uncovering the myriad ways these compounds can impact health and wellness.
Description: CBGA is often referred to as the “stem cell” of cannabinoids.
This is where the story of many cannabinoids begins. CBGA is the chemical precursor from which many other cannabinoids are synthesized, including THC, CBD, and CBG.
In its natural state, it’s a foundational compound in the cannabis plant’s biochemistry, playing a crucial role in the formation of many other cannabinoids.
Effects: The potential health benefits of CBGA are just beginning to be uncovered.
Early research points to a range of possibilities, but the full extent of its effects remains a tantalizing mystery.
As the starting point for so many other cannabinoids, understanding CBGA could unlock new insights into the entire cannabinoid system and its myriad effects on the human body.
Description: Meet CBCA, the acidic form of CBC and another key player in the cannabinoid family.
Much like CBGA, CBCA is a precursor molecule, serving as a building block for other cannabinoids.
It’s a bit of a behind-the-scenes actor in the cannabinoid world, less famous but crucial in the cannabis plant’s chemistry.
Effects: While CBCA may not be as well-studied as some of its counterparts, it holds promise for future medical applications.
The potential of CBCA lies in the unknown, inviting researchers to explore its properties and possible health benefits.
As the study of cannabinoids continues to evolve, compounds like CBCA may soon step into the limelight with newfound applications and benefits.
As we conclude our journey through the world of cannabinoids, one thing becomes abundantly clear: the cannabis plant is a complex and multifaceted organism, brimming with compounds that offer a wide range of effects and potential benefits.
From the well-known THC and CBD to the lesser-known but equally intriguing CBCA and CBGA, each cannabinoid presents a unique piece of the puzzle.
The ongoing research into cannabinoids is a testament to the evolving understanding of these compounds.
With each study and discovery, we gain a deeper appreciation for the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids.
They offer a window into a future where natural compounds could play a significant role in health and wellness.
As we continue to explore and understand these compounds, it’s crucial to approach cannabis and its derivatives with an open mind and a respect for their complexity.
The potential of cannabinoids is vast, and the journey of discovery is just beginning. Let’s keep our eyes open to the possibilities that lie ahead in this exciting and ever-evolving field.

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]