Our bodies are incredible machines, finely tuned to perform an array of complex functions. One of the systems that helps regulate our internal environment is the endocannabinoid system (ECS). This system is like a conductor of an orchestra, ensuring that everything works in harmony. It plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and regulating various physiological processes, including appetite, mood, and sleep. At the heart of this system are the CB1 and CB2 receptors in the brain, which are like the musicians in our metaphorical orchestra, responding to different cues to create a beautiful symphony.
A. Brief overview of the endocannabinoid system
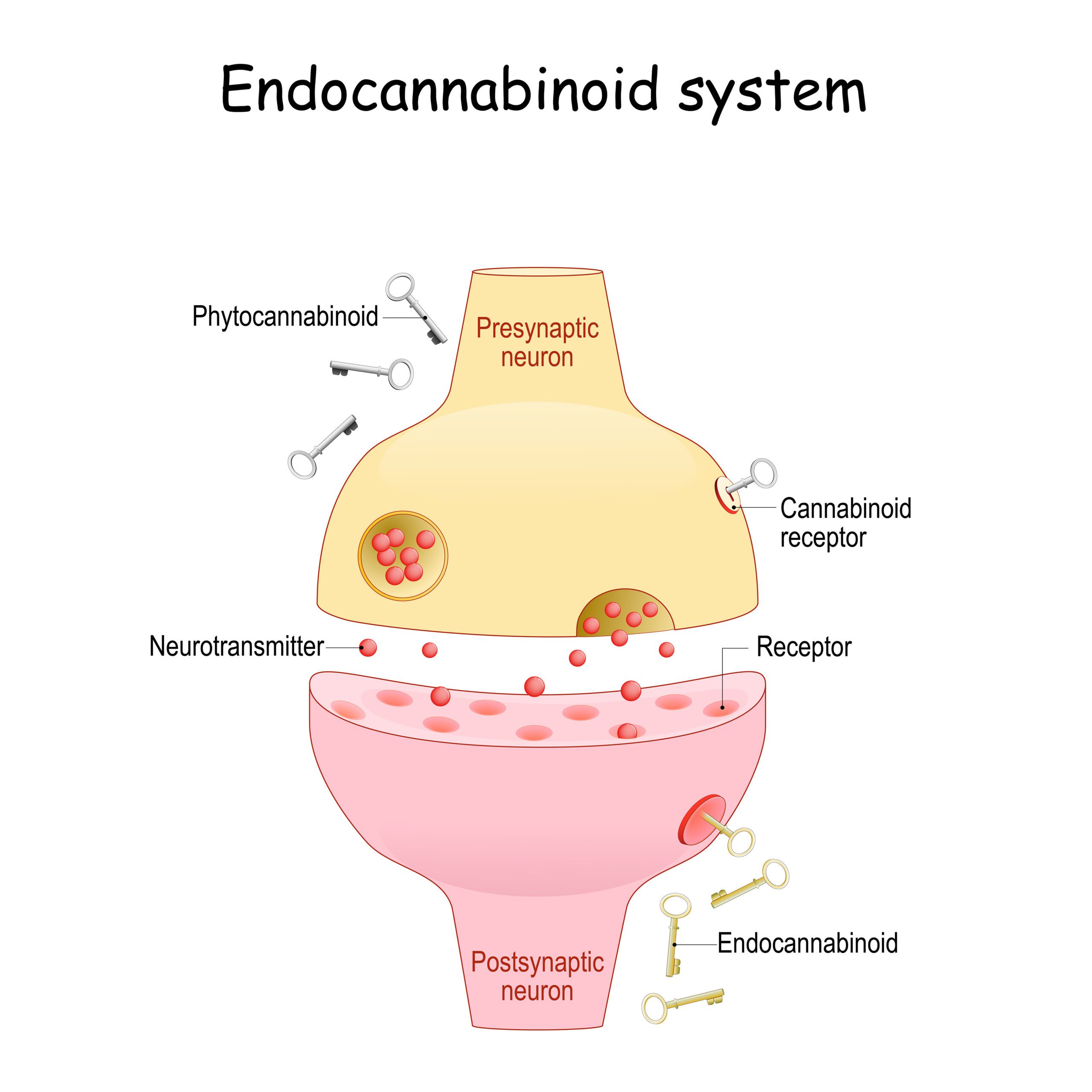
The ECS consists of endocannabinoids, which are naturally occurring compounds in the body, and their corresponding receptors. These receptors are found throughout the body but are particularly concentrated in the brain. When activated, they help maintain homeostasis, or balance, by regulating various physiological processes.
B. Importance of CB1 and CB2 receptors in the brain
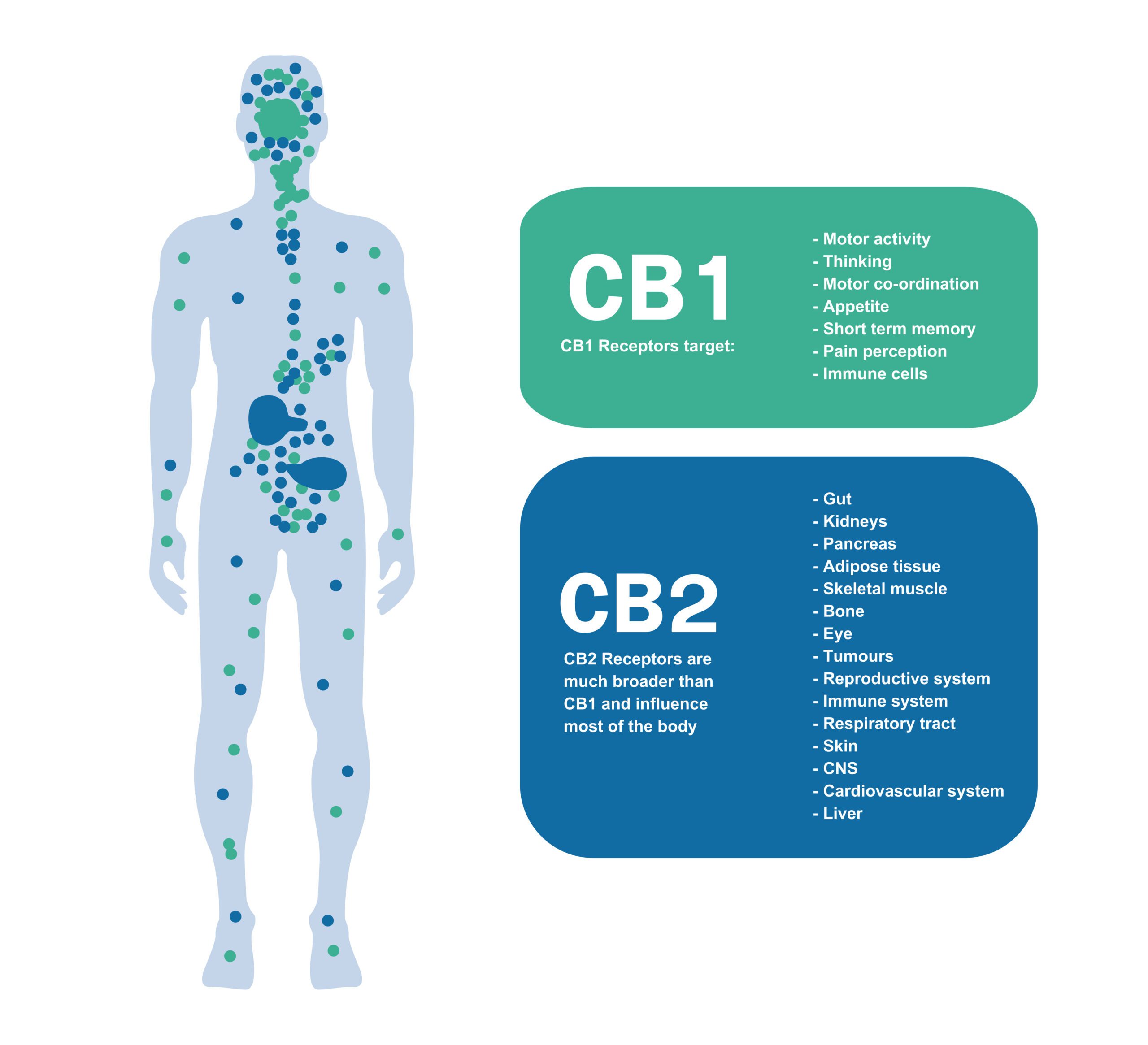
CB1 and CB2 receptors are crucial components of the ECS. They act as the “gatekeepers,” controlling the flow of information and ensuring that everything works in harmony. These receptors are involved in a range of functions, from regulating mood and sleep to controlling appetite and pain perception.
CB1 Receptors
A. Location and function of CB1 receptors in the brain
CB1 receptors are found throughout the brain, but they are particularly concentrated in areas involved in appetite regulation, such as the hypothalamus and the limbic system. These receptors play a crucial role in controlling the release of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals between nerve cells. When activated, CB1 receptors help to enhance the pleasure and reward associated with eating, making food more appealing.
B. Role of CB1 receptors in appetite regulation
When activated, CB1 receptors trigger a series of events that ultimately lead to an increase in appetite. They enhance the release of certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, that are involved in the pleasure and reward associated with eating. This makes food more appealing and stimulates the desire to eat.
Marijuana contains a compound called THC, which is known to activate CB1 receptors. When this happens, it triggers the same series of events that lead to an increase in appetite, resulting in the famous “munchies” that many users experience.
C. Research on CB1 receptors and eating behavior
Research on animals has shown that when CB1 receptors are activated, it increases food intake. For example, studies on rats have shown that they eat more when given compounds that activate CB1 receptors.
Studies on humans have also shown a link between CB1 receptors and appetite. For example, research has found that people with certain genetic variations in their CB1 receptors have different eating behaviors. This suggests that CB1 receptors play a crucial role in regulating appetite in humans as well.
CB2 Receptors
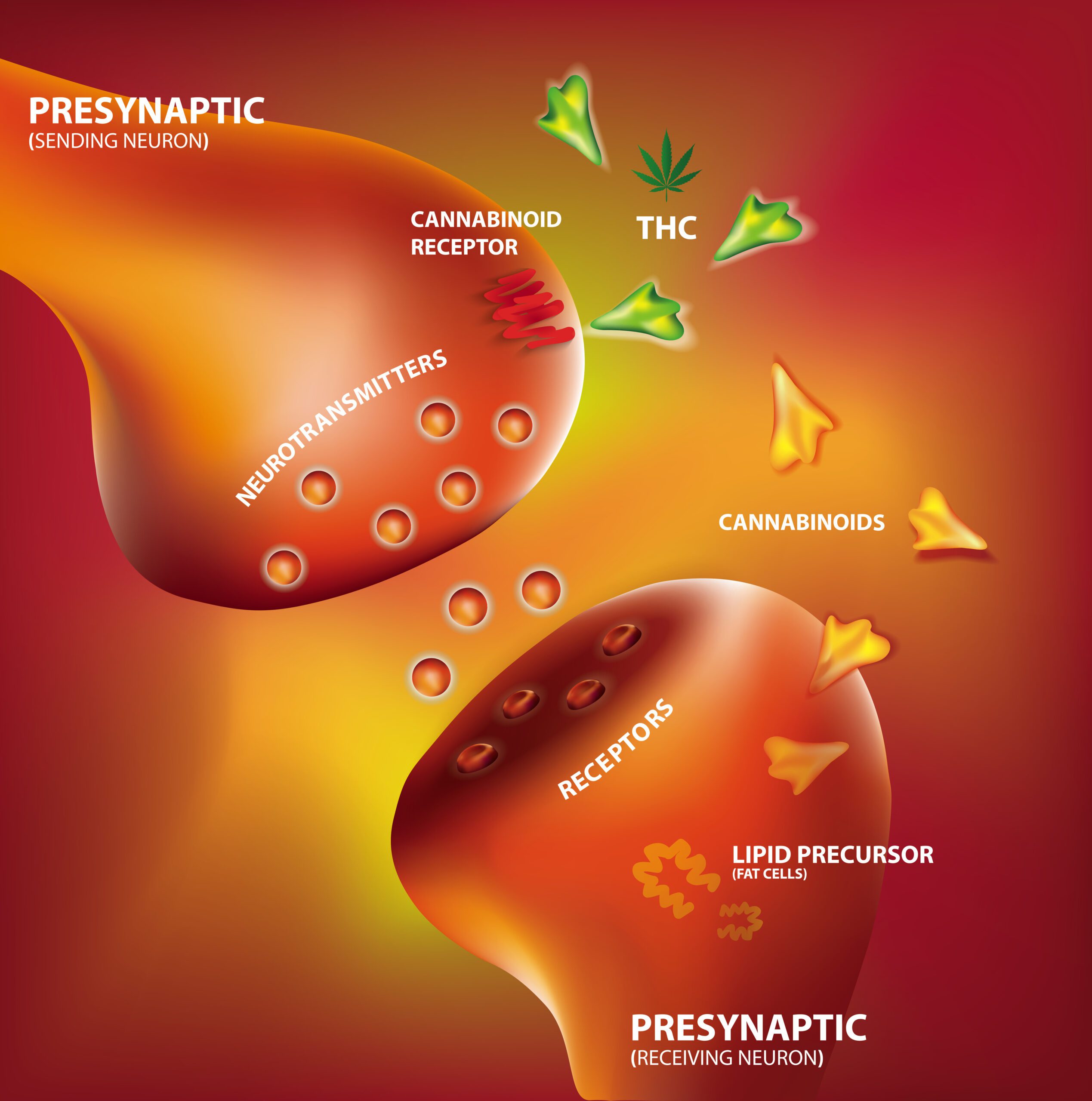
While their sibling, the CB1 receptor, may steal the spotlight when it comes to appetite regulation, CB2 receptors also play a role in this complex dance.
A. Location and function of CB2 receptors in the brain
Unlike CB1 receptors, CB2 receptors are less prevalent in the brain. However, they are found in various other parts of the body, such as the immune system. Their primary function is to modulate inflammation and immune responses.
B. Role of CB2 receptors in appetite regulation
The role of CB2 receptors in appetite regulation is not as well understood as that of CB1 receptors. However, some studies suggest that they may play a part in reducing inflammation and regulating metabolism, both of which can influence eating behavior.
Research on the role of CB2 receptors in appetite regulation is still in its infancy. However, there are some promising findings that suggest these receptors could be a target for future therapies aimed at regulating appetite and treating obesity.
C. Differences between CB1 and CB2 receptors in relation to appetite
The key difference between CB1 and CB2 receptors in relation to appetite is the way they influence eating behavior. CB1 receptors primarily affect appetite by enhancing the pleasure and reward associated with eating, while CB2 receptors may influence appetite by regulating metabolism and inflammation.
Potential therapeutic applications
As our understanding of the endocannabinoid system and its role in appetite regulation continues to grow, the potential therapeutic applications of manipulating CB1 and CB2 receptors are becoming more apparent.
A. How manipulating CB1 and CB2 receptors could be used to treat eating disorders
By targeting CB1 and CB2 receptors, it may be possible to develop therapies that can help treat eating disorders such as anorexia and bulimia. These therapies could work by regulating appetite and normalizing eating behavior.
B. Current research on using CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists/antagonists for appetite regulation
Researchers are currently investigating the potential of using CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists (which activate the receptors) and antagonists (which block the receptors) to regulate appetite. Some studies have shown that CB1 receptor antagonists can reduce food intake and lead to weight loss, while CB2 receptor agonists may have anti-inflammatory effects that could be beneficial in treating obesity-related conditions.
Conclusion
In the fascinating and complex world of the human body, the endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and harmony. The CB1 and CB2 receptors, like musicians in an orchestra, respond to different cues to help regulate a range of physiological processes, including appetite and eating behavior.
A. Summary of key points
B. Potential future research directions
There is still much to learn about the role of CB2 receptors in appetite regulation, and future research could focus on better understanding how these receptors influence eating behavior. Additionally, more studies are needed to investigate the potential therapeutic applications of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists/antagonists in the treatment of eating disorders and obesity.
C. Final thoughts on the importance of understanding CB1 and CB2 receptors in relation to appetite and eating
Understanding the role of CB1 and CB2 receptors in appetite regulation is crucial for developing new therapies to treat eating disorders and obesity. By unlocking the secrets of these receptors, we can harness the power of the endocannabinoid system to bring balance and harmony to the complex world of appetite and eating behavior.

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]