Have you ever wondered why cutting calories doesn’t always lead to weight loss?
November 13, 2023
 789
789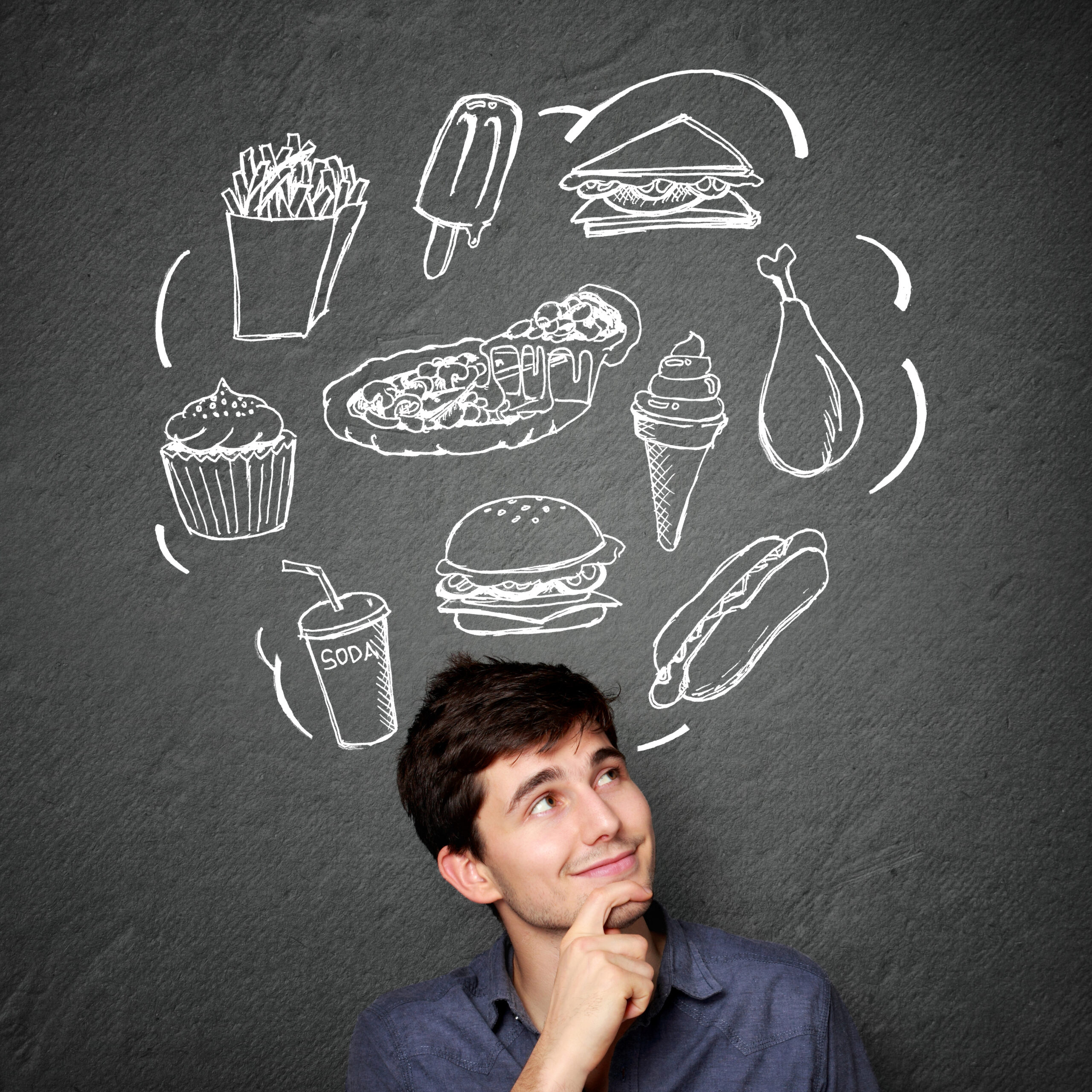 
Traditional dieting wisdom tells us that less food equals more weight loss. However, recent insights suggest that this equation isn’t as simple as it seems.
A comprehensive study by the National Institute of Health has shown that reducing calorie intake might not be the golden ticket to weight loss we once believed.
The reason lies in our body’s complex metabolic processes, which can adapt to lower calorie intake and, in turn, slow down metabolism.
Here is how it works….
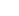
Drastic caloric reduction can significantly impact two key hormones in your body: leptin and ghrelin.
These hormones play essential roles in regulating appetite and energy balance, and they’re deeply affected by how much you eat.
Leptin, often called the “satiety hormone,” is produced by fat cells and signals to your brain that you have enough energy stored. It helps to suppress appetite and can make you feel full.
When you cut calories dramatically, your body produces less leptin, leading to decreased feelings of fullness and a potential increase in appetite.
Ghrelin, known as the “hunger hormone,” is released primarily in the stomach and signals hunger to the brain.
When your stomach is empty, ghrelin levels increase, telling your brain it’s time to seek out food. Drastic caloric reduction causes ghrelin levels to rise, which can make you feel hungrier even though you’re trying to eat less.
This hormonal response can create a challenging cycle for those trying to lose weight. As you eat less, your body’s production of leptin decreases, and ghrelin increases, which can lead to increased hunger and a stronger appetite.
This biological reaction can make it very difficult to stick to a low-calorie diet and can cause some people to regain weight after an initial loss, often referred to as “yo-yo dieting.”

This finding is a game-changer in the weight loss industry. It means that instead of focusing solely on cutting calories, we should be looking at the type of calories, the timing of our meals, and how we can keep our metabolism fired up and ready to burn fat.
So, what does this mean for you?
It means that a diet like the Metabolic Confusion Principle, which focuses on varying caloric intake and still allow you to eat your favorite foods could be the answer to effective weight loss. It’s designed to prevent the metabolic slow-down that often accompanies traditional dieting.
Say goodbye to the days of restrictive eating that leads nowhere. Embrace a method backed by science and research, one that understands and works with your body’s natural rhythm.
It’s time to rethink weight loss — and the Metabolic Confusion Principle is here to lead the charge.

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]