
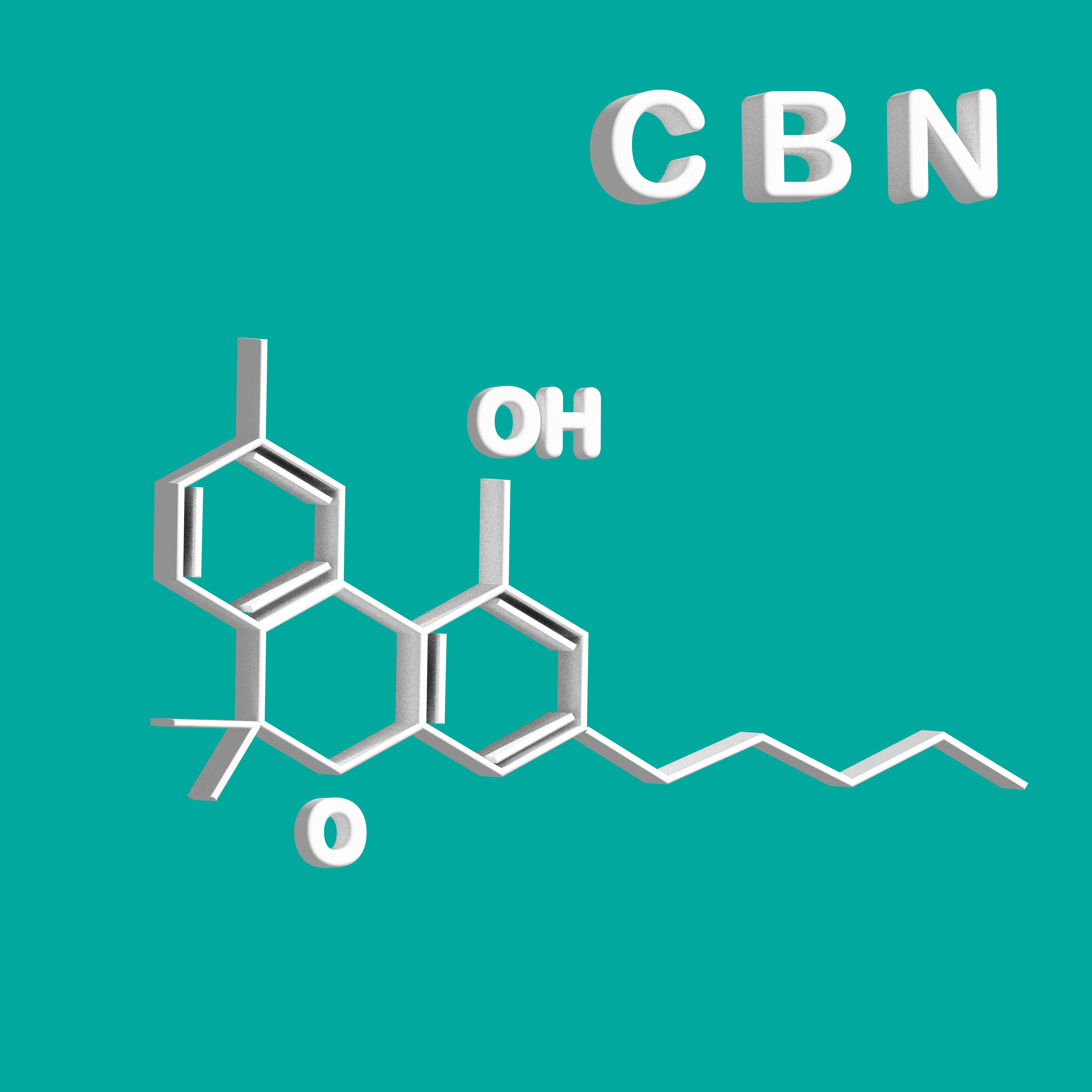
In the ever-expanding world of cannabinoids, CBN (Cannabinol) emerges as a lesser-known yet intriguing compound derived from the cannabis plant.
Unlike its famous counterparts, THC and CBD, CBN has quietly garnered attention for a specific attribute: its potential to promote deeper and longer sleep.
With a growing interest in natural sleep aids, CBN is increasingly becoming a topic of interest for those seeking a restful night’s sleep, drawing attention from researchers, healthcare professionals, and individuals alike.

CBN is a unique cannabinoid with a fascinating process of creation and a distinct set of properties.
The Transformation from THC to CBN
CBN originates from the degradation of Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the well-known psychoactive component of cannabis.
As THC ages and is exposed to oxygen and light, it breaks down and transforms into CBN.
This process is natural and occurs over time, resulting in higher levels of CBN in older cannabis.
Properties and Distinctions of CBN
Unlike THC, CBN does not produce intoxicating effects, making it an appealing option for those who wish to avoid the ‘high’ associated with THC.
CBN shares some similarities with Cannabidiol (CBD), another non-psychoactive cannabinoid, but it is distinct in its chemical structure and effects.
The interest in CBN primarily revolves around its potential as a sedative, with anecdotal reports and preliminary research suggesting its efficacy in promoting better sleep quality.

The potential of CBN as a sleep aid has garnered interest in the scientific community, though research in this area is still in its nascent stages.
Understanding CBN’s Effect on Sleep
CBN is believed to interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in regulating various physiological processes, including sleep.
Some studies suggest that CBN may have sedative effects, though these are often based on anecdotal evidence or are in the early stages of research.
Research Findings on CBN’s Effectiveness
One of the challenges in studying CBN’s impact on sleep is the variability of cannabis compounds and their interactions.
However, initial studies and user reports indicate a potential for improved sleep quality.
Research specifically focusing on CBN is limited, and more comprehensive studies are needed to conclusively determine its effectiveness and optimal dosages for sleep enhancement.

In comparison to other sleep aids, CBN stands out for its unique properties and potential benefits.
CBN vs. Traditional Sleep Aids
Unlike pharmaceutical sleep aids, CBN does not seem to have significant addictive properties or produce a ‘hangover’ effect, making it a potentially safer alternative for long-term use.
Many common sleep medications can have side effects like dizziness, gastrointestinal issues, and next-day drowsiness, which are less commonly associated with CBN.
Advantages Over Natural Sleep Aids
Compared to natural sleep aids such as melatonin, valerian root, or chamomile, CBN may offer a more pronounced sedative effect for some individuals.
CBN’s non-intoxicating nature is a significant advantage for those seeking a natural sleep aid without the psychoactive effects associated with THC.
CBN’s potential in the realm of sleep aids lies in its unique qualities, setting it apart from both pharmaceutical and natural alternatives.
Its non-intoxicating, potentially sedative nature positions it as an intriguing option in the quest for better sleep.
Incorporating CBN into a sleep routine can be a game-changer for those struggling with sleep issues, but it’s important to understand how to use it effectively.
Incorporating CBN into Your Routine
Start by integrating CBN into your nightly routine gradually.
Begin with a low dose to see how your body responds before increasing the amount.
Consistency is key.
Use CBN at the same time each night to help regulate your sleep cycle.
Forms of CBN Products
CBN is available in various forms, including oils, edibles, and capsules, each offering different methods of consumption and onset times.
Oils placed under the tongue (sublingual) typically have a quicker onset, while edibles and capsules may take longer to take effect but often provide a longer duration of sleep aid.
Recommended Dosages
The optimal dosage of CBN can vary depending on the individual and the product.
Starting with the manufacturer’s recommended dose is advisable.
As with any supplement, it’s important to monitor your body’s response and adjust the dosage accordingly.
CBN stands out as a promising natural aid in the pursuit of improved sleep quality.
Its potential to provide deeper, more restful sleep without the significant side effects associated with traditional sleep medications makes it an attractive option for many.
Recapping CBN’s Potential
The unique properties of CBN, including its non-intoxicating nature and potential sedative effects, position it as a noteworthy alternative in the natural sleep aid market.
While research into CBN is ongoing, early indications suggest that it could be a valuable tool in addressing sleep quality issues.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
As with starting any new supplement regimen, it’s crucial to consult with healthcare professionals.
This is particularly important for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking other medications.
A healthcare provider can offer guidance on appropriate dosages and ensure that CBN use is safe and effective for your specific needs.
In conclusion, CBN offers an exciting possibility for those seeking natural solutions to sleep challenges.
Its role in enhancing sleep quality continues to gain interest, and with proper use and guidance, it could be an excellent addition to your sleep routine.

A new study suggests that a widely used sugar substitute found in diet sodas, chewing gum, and low-sugar yogurt may elevate insulin levels. This could increase the long-term risk of heart disease. “Artificial sweeteners have infiltrated nearly all types of food, making it crucial to understand their long-term health effects,” said Yihai Cao, senior author […]

Diet Coke has long been a fan-favorite among soda lovers who want a fizzy, guilt-free alternative to traditional soft drinks. While its zero-calorie, zero-sugar label makes it seem like a healthier option, the reality is far more concerning. Despite its undeniable popularity, Diet Coke’s nutritional profile has raised red flags among health experts for years. […]

New study shows that embracing an anti-inflammatory, plant-forward diet can support cognitive function and help reduce the risk of dementia. What You Eat Shapes Your Brain The food you eat doesn’t just impact your body—it also affects your brain. Research suggests that eating an anti-inflammatory, plant-based diet can help improve memory, focus, and overall brain […]